Endotracheal intubation complications can be intraoperative, postoperative or delayed.
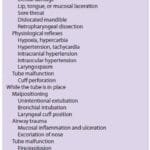
The following are the immediate intubation complications that are commonly seen:
- Esophageal intubation: This is a hazardous complication. Can be done as a mistake. If not detected in time can cause severe hypoxia and even death. This can be easily be detected by measuring carbon dioxide gas in expired gases by Capnography.
- Ischemia, edema and necrosis at local site (especially with red rubber tubes).
- Aspiration (if cuff is not properly inflated or an uncuffed tube is used).
- Bronchial intubation and collapse of other lung. This results in the ventilation of only one lung, most commonly the right lung. This is very common among the intubation complications.
- Tracheal tube obstruction by secretions, kinking. Again if not detected in time can cause hypoxia. This can be detected by increase in the Airway pressures and resistance in the bag. These are the more dreadful and can result in death.
- Accidental extubation, especially during changing the position of the patient for surgery.
- Trauma to gums, lip, epigiottis, pharynx, larynx and nasal cavity (in nasal Intubation) are easily avoidable intubation complications. Incisors can be damages by faulty technique of intubation, where leverage of the incisors is done.
- Reflex disturbances like laryngospasm, bronchospasm and breath holding.
- Intubation complications of the heart include cardiac arrhythmias, hypertension or even cardiac arrest.

For post operative complications on intubation, what is the time factor for relief of swallowing difficulties-paralysis of vocal cords, etc.
Do you need the anesthesia report?
Thank you.